
Hand joint pain may result from muscle strain or may be a sign of a dangerous systemic disease. Fortunately, the latter are much less common. Very often, doctors are faced with injuries and problems of the ligament system, which respond well to local treatment. When hand joints hurt, the causes and treatment are quite varied. To treat hand pathology it is important that the patient asks for help promptly, especially if the fingers are deformed: the longer they remain in a forced position, the more difficult it is to restore their function. In the article we will talk about possible diagnoses for which the joints of the hands hurt, what to do, how to treat such conditions.
Pain in the small joints of the fingers: causes
Patients who experience numbness, clicking, or pain in the finger joints during flexion, extension, or at rest may have a variety of diagnoses.
"Breaking finger, " also known as stenosing ligamentitis or Knott's disease
One of the most common causes of hand pain. This is a benign pathology in which it is very difficult to independently straighten the finger from a bent position. The disease is common among both women and men and is associated with damage to the annular ligament of the hand. There is a feeling that the finger is "stuck" in one position. Usually the joint of the middle finger of the right hand hurts, as well as the ring finger or thumb. In left-handed people, the left hand is more often affected.
Risk factors include:
- Overstrain of the wrist flexor muscles. This can happen when working on a computer for long periods of time, driving long distances, carrying heavy bags, playing the guitar, experiencing repeated blunt trauma to the hand, or working with tools that must be held securely in the hand, such as construction.
- Metabolic disorders in the body: diabetes mellitus, decreased thyroid function - hypothyroidism.
- Smoking: Nicotine damages small blood vessels and nerves.
- Previous injury to the palm or base of the finger.
Hand injury
This includes fractures, bone cracks, joint dislocations, ligament and muscle tears and sprains. A condition called hammertoe is common. This finger is bent and hurts a lot when you try to straighten it. It is distinguished from the "snapping finger" by the following characteristics:
- Reason for appearance. "Hammer finger" is a consequence of an injury, for example, caused by a strong blow to the tip of an extended finger, for example hit by a ball while playing basketball.
- Localization of the flexion. The hammertoe is bent at the distal interphalangeal joint, which is the small joint of the finger closest to the nail. The "trigger finger" is bent at the proximal interphalangeal joint, the second joint of the finger from the nail, or at the metacarpophalangeal joint, which connects the finger and the palm itself.
- The hammertoe often becomes swollen, blue and deformed, especially if there is a fracture of the phalanx.
Osteoarthritis
It is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the joints, a common pathology in patients over the age of 40, especially in women. The cartilaginous tissue that forms the joint is destroyed and the amount of fluid inside it decreases. As a result, the joint becomes "dry" and its mobility decreases. In later stages, the bones that form the joint are also destroyed and "growths" – osteophytes – may appear on them. The interphalangeal joints of the fingers are usually affected. It is difficult for the patient to make a fist or hold heavy objects, which significantly interferes with everyday life.
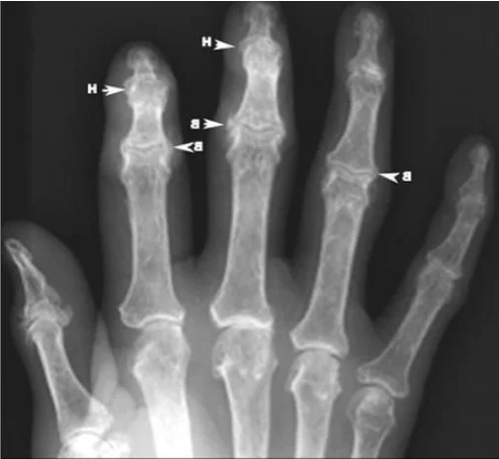
Rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis
These are autoimmune diseases. The metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints are most often affected. Because these diseases are systemic, meaning they cause changes throughout the body, the joints in both hands typically become painful and swollen. In addition, these patients often have other symptoms: weakness, fever, loss of appetite. Severe rheumatoid arthritis can have extra-articular manifestations, involving the heart, lungs, eyes, blood vessels and other organs. Despite its name, psoriatic arthritis can occur in the absence of symptoms of psoriasis, a skin disease.
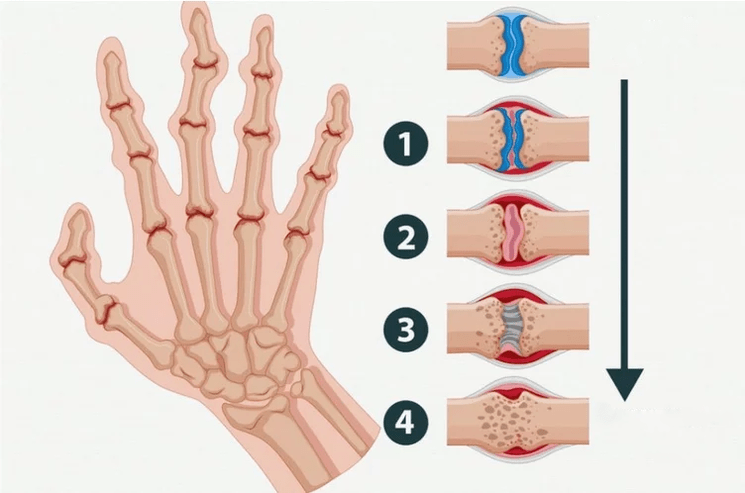
Gout and pseudogout
Metabolic disorders in which hard crystals are deposited in the joints. In gout, uric acid, a product of purine metabolism, is deposited in the form of crystals. Purines are formed inside the body and also come from food. Gout crystals can appear not only inside joints, but also under the skin and in tendons. The body reacts to them with severe inflammation. Pseudogout is similar to gout in its symptoms, but is caused by the deposition of a different substance: calcium pyrophosphate. Both diseases are treated with medications, although the medications are slightly different.
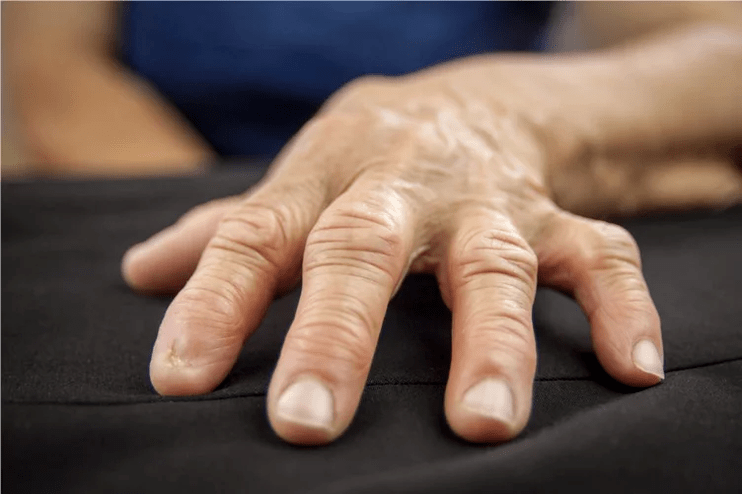
Tumors and cysts
This is a very rare pathology; the vast majority of hand tumors are benign. Cysts can appear in bone tissue and joints. They cause pain and, when large, impair the range of motion of the joints.
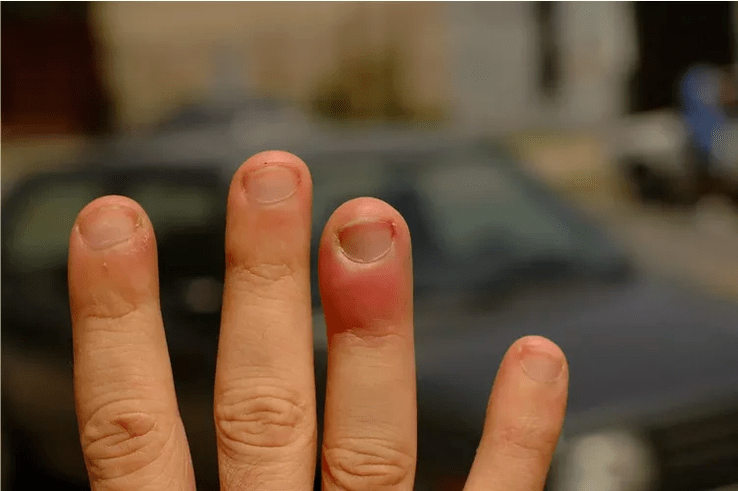
Infectious diseases of the fingers
The most common: the criminal and its variety - paronychia. This is an infection of the periungual tissues. Other infections include:
- cellulite - inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue,
- lymphangitis - inflammation of the lymphatic vessel,
- abscesses - collections of pus,
- osteomyelitis - inflammation of the bone.
Patients with hand infections usually report previous minor trauma. The risk of these diseases increases if a person has a weakened immune system.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Caused by compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel, formed by the wrist bones, ligaments and tendons. Women suffer from this syndrome more often than men. Conditions in which the likelihood of developing the disease increases: thyroid disease, pregnancy, obesity, diabetes. Constant work with prolonged holding of the wrist in the extended position often becomes a provoking factor. This is especially true for people whose professions involve assembling small parts, such as tailors or surgeons, or working on a computer. Symptoms appear in the fingers innervated by the median nerve: thumb, index finger, middle finger and half of the ring finger adjacent to them. Usually it is not just pain, but also numbness, tingling, tingling and sometimes weakness in the hand.
Dupuytren's contracture or palmar fibromatosis
With this disease, it is impossible to completely straighten the fingers, they are in a forced semi-bent position, resulting in a violation of the functioning of the hand. First, dense cords of connective tissue are formed in the palmar tendons, then they are shortened. Most often, the disease appears in men over 50 years of age and has a clear hereditary predisposition. As with many other hand diseases, the risk increases due to diabetes, smoking and occupational risks.
The list of possible diagnoses of pain in the joints of the hand also includes a number of more rare conditions: vibration disease, vasculitis, etc. Given this diversity, it is better not to delay contact with a specialist.
Symptoms
The symptoms depend on the disease and the causes that caused it. The main sign of problems with the joints of the hand and its other structures is pain, but it is important to evaluate all its features:
- The onset of pain, which can be acute or gradual.Diseases caused by degenerative changes and excessive strain of the ligament system are characterized by a gradual onset, since the development of these processes takes time. Autoimmune diseases can occur gradually or acutely. Flares of gout and pseudogout occur suddenly, reaching peak symptoms within a few hours. Trauma is also associated with sharp, sharp pain.
- Timing and factors that determine the appearance or intensification of pain during the day.In carpal tunnel syndrome the hand may hurt at night; in osteoarthritis the pain is stronger after putting stress on the joints; in rheumatoid arthritis the pain is most pronounced in the first 30 minutes after waking up or after prolonged inactivity.
In addition to pain, patients may notice other associated symptoms, including:
- Characteristics of flexion and extension of the joints: with the "trigger finger" the joint is locked in flexion, but can be carefully transferred to an extended position, while the "hammer finger" and contracture cannot be completely straightened. With rheumatoid arthritis, thickening of the fingers in the joints and their deformation can be observed. If there is a pathology of the ligaments, nodules can be felt in their composition.
- Stiffness and limitation of joint movements.
- With gout and autoimmune arthritis, the patient will notice redness and swelling, the joint will be warm to the touch - these are symptoms of inflammation.
- If the nerves are damaged, numbness, goosebumps, tingling, and reduced sensitivity to heat, cold, and touch may occur.
- With vasculitis - inflammation of the blood vessels - the fingers often turn white or blue.
- In many diseases, weakness in the hand can be observed: this indicates nerve damage and also occurs in cases of injury.
- General symptoms such as weakness, fever and problems with other organs whose cause is unknown indicate the systemic nature of the disease. In these cases it is best to consult a doctor immediately.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with a consultation with a specialist, who asks in detail about complaints, the presence of concomitant and hereditary diseases. Next, the doctor must examine the patient and palpate the hand. In some cases, these manipulations are sufficient to make a diagnosis. But to confirm and clarify this, further studies are required. Can be:
- X-ray of the hands in various projections- the most commonly used and accessible method for assessing the condition of bones and joints. It will be asked if there is a suspected fracture, foreign body, developmental anomaly, tumor or cyst, as well as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis on an x-ray is manifested by a decrease in the joint cavity, as well as the presence of bone growths - osteophytes.
- CT scan(CT). Used to better visualize complex fractures and evaluate joint conditions.
- Ultrasound of the soft tissues and joints of the hand. It allows you to view ligaments, tendons, nerve trunks and the state of the joints.
- magnetic resonance imaging. The method provides clear layer-by-layer images of all structures of the hand. The main indications for use are ligament and tendon injuries.
- Electroneuromyography. This method is necessary to evaluate the conduction of nerve impulses. It is used if carpal tunnel syndrome is suspected.
- Blood analysis.Most often this is:
- metabolic indicators - for example, glycated hemoglobin and blood sugar in diabetes, as metabolic diseases affect the condition of nerves, small vessels and ligaments.
- tests for the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, rheumatoid factor, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies.
Which doctor should I contact?
Diseases of the hand structures, due to their enormous diversity, often require consultation with specialists of different profiles. Initially, if there has been no real injury, you should see a therapist; if an injury has occurred, you should consult a traumatologist.
Autoimmune diseases are treated by rheumatologists. Diagnosis and treatment of hand injuries and tumors are carried out by traumatologists and orthopedic surgeons. Consultation with an endocrinologist will be necessary for metabolic disorders. If you notice weakness and numbness in your hand, you should consult a neurologist.
How to relieve finger joint pain
Treatment can be surgical or conservative.
- Surgical treatmentnecessary for purulent processes on the hand, as well as for complex lesions. Open wounds also require surgical treatment. Any wound is a source of infection, and such patients are prescribed antibiotics and debridement. Closed fractures can be treated conservatively. They begin with rigid fixation of the fracture site: for 7-10 days for non-displaced fractures and for 3 weeks for displaced fractures. After that, the patient wears a special orthosis on the hand until the bone is completely restored, usually 4-10 weeks, sometimes longer.
Conservative treatmentfor autoimmune diseases affecting the joints of the hand, it is special: it is based on drugs that suppress the immune response and is prescribed by a rheumatologist. For musculoskeletal problems, systemic drug treatment is used as part of complex therapy. For hand joint pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be indicated to relieve pain and inflammation. Local methods of influence give a good effect:
- Injectionscorticosteroids in the joints of the hand, in the tendons. They effectively relieve inflammation, but have side effects, so they must be used according to strict indications.
- Soft fixation of the handusing orthotics or an elastic bandage. The fixation position depends on the diagnosis.
- Exerciseson the muscles of the hand, which a specialist will help you choose depending on the pathology.
- Acupuncture.The method involves the insertion of sterile needles into biologically active points, which relieves pain and improves joint mobility.
- Shock wave therapy.In recent years it has gained popularity in the treatment of ligament problems. Effective and safe for the treatment of "breaking finger", deforming osteoarthritis, it reduces the likelihood of recurrence, improves joint mobility and the functionality of the hand as a whole.
- Kinesiotaping.This involves gluing special tapes to the hand, which help stabilize the joint in a comfortable position. This way you recover faster.
- Laser therapy.It reduces pain and helps in the restoration of cartilage, which is extremely important for osteoarthritis.
- Magnetotherapy. Aimed at reducing pain, inflammation and swelling.
Consequences
Most patients with hand injuries and degenerative processes, broken fingers and carpal tunnel syndrome are able to restore joint function and return to their normal lifestyle. The main role in the prognosis of the disease is played by early consultation of the doctor, correct use of the bandage, orthosis, if indicated, and compliance with the prescribed recommendations. If the joints of the hand are left untreated for a long time, deformations are possible that cannot be completely eliminated. Contact a specialist as soon as you have complaints about the condition of your hand and he will select the necessary therapy for you.
Prevention
- Address common risk factors.The risk of musculoskeletal hand problems increases with metabolic disorders, smoking and hormonal disorders. It is important to maintain a normal blood sugar level, especially if you have already been diagnosed with diabetes. A special diet is recommended for gout patients, and some are prescribed anti-gout medications. It will be useful to periodically check the status of the thyroid. A decrease in its function negatively affects the immune system and the entire body.
- Take care of your hand if the risk of joint disease increases.For example, if your job involves overloading your hands, try to secure the most comfortable position, don't keep your hands constantly bent, let them rest and do some warming up. Play sports in special gloves, monitor the condition of the skin and nails so that the infection does not penetrate the tissues of the hand. Regularly undergo preventive examinations with doctors.
Follow the recommendations listed and this will help reduce the risk of hand problems.



















